NSK New Bearing Doctor
When a rolling bearing is damaged during machine operation, the entire machine or equipment may seize or malfunction. Since bearings that fail prematurely or unexpectedly cause trouble, it is important to be able to identify and predict failure beforehand, if possible, so that preventive measures can be adopted.
This pamphlet contains explanations about correct bearing handling, mounting, lubrication, and maintenance to prevent premature failure together with color photos of bearing failures. Most premature bearing failures can be avoided. Causes include improper mounting, mishandling, poor lubrication, entry of foreign particles/contamination and abnormal heat generation.
If all conditions are known both before and after the failure, including the application, operating conditions and the environment, then a countermeasure can be determined by studying the nature of the failure and its probable causes.

In general, if rolling bearings are used correctly, they will survive to their predicted fatigue life. Bearings, however, often fail prematurely due to avoidable mistakes. In contrast to fatigue life, this premature failure is caused by improper mounting, mishandling, poor lubrication, entry of foreign matter or abnormal heat generation.
If all conditions are known for the times both before and after the failure, including the application, the
operating conditions, and environment, then a measure can be determined by studying the nature of the failure and its probable causes. A successful measure will reduce similar failures or prevent them from happening again.



Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Flaking
Damage Cond
Flaking occurs when small pieces of bearing material are split off from the smooth surface of the raceway or rolling elements due to rolling fatigue, thereby creating regions having rough and coarse texture.
Possible Cause
- Excessive load
- Poor mounting (misalignment)
- Moment load
- Entry of foreign debris, water penetration
- Poor lubrication, Improper lubricant
- Unsuitable bearing clearance
- Improper precision for shaft or housing, unevenness in housing rigidity, large shaft bending
- Progression from rust, corrosion pits, smearing,dents (Brinelling)
Countermeasure
- Reconfirm the bearing application and check the load conditions
- Improve the mounting method
- Improve the sealing mechanism, prevent rusting during non-running
- Use a lubricant with a proper viscosity, improve the lubrication method
- Check the precision of shaft and housing
- Check the bearing internal clearance

Part: Inner ring of an angular contact ball bearing
Symptom: Flaking occurs around half of the circumference of the raceway surface
Cause: Poor lubrication due to entry of cutting coolant into bearing

Part: Inner ring of an angular contact ball bearing
Symptom: Flaking occurs diagonally along raceway
Cause: Poor alignment between shaft and housing during mounting
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Flaking

Part: Balls
Symptom: Flaking of ball surface
Cause: Dents due to shock load while stationary

Part: Outer ring
Symptom: Flaking of raceway surface at ball pitch
Cause: Dents due to shock load while stationary

Part: Rollers of a cylindrical roller bearing
Symptom: Premature flaking occurs axially on the rolling surfaces
Cause: Scratches caused during improper mounting
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Flaking
Damage Condition
Flaking occurs when small pieces of bearing material are split off from the smooth surface of the raceway or rolling elements due to rolling fatigue, thereby creating regions having rough and coarse texture.
Possible Cause
- Excessive load
- Poor mounting (misalignment)
- Moment load
- Entry of foreign debris, water penetration
- Poor lubrication, Improper lubricant
- Unsuitable bearing clearance
- Improper precision for shaft or housing, unevenness
in housing rigidity, large shaft bending - Progression from rust, corrosion pits, smearing,
dents (Brinelling)
Countermeasure
- Reconfirm the bearing application and check the load conditions
- Improve the mounting method
- Improve the sealing mechanism, prevent rusting during non-running
- Use a lubricant with a proper viscosity, improve the lubrication method
- Check the precision of shaft and housing
- Check the bearing internal clearance
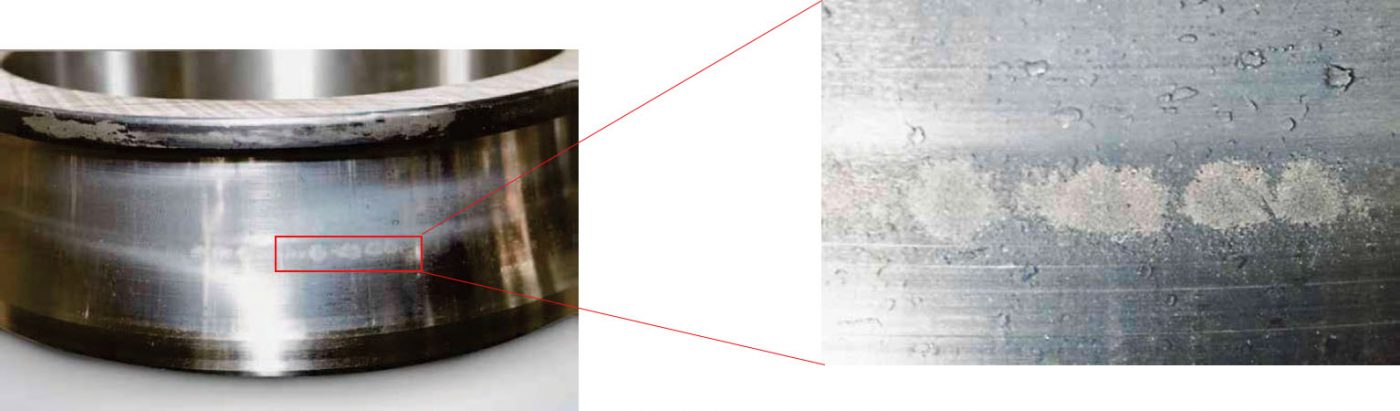

Part: Inner ring of a spherical roller bearing
Symptom: Round shaped peeling pattern occurs on the
center of the raceway surface
Cause: Poor lubrication
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Peeling

Part: Convex rollers
Symptom: Round shaped peeling pattern occurs on the center of the rolling surfaces
Cause: Poor lubrication

Part: Outer ring of a spherical roller bearing
Symptom: Peeling occurs near the shoulder of the raceway over the entire circumference
Cause: Poor lubrication
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Scoring
Damage Condition
Scoring is surface damage due to accumulated small seizures caused by sliding under improper lubrication or under severe operating conditions. Linear damage appears circumferentially on the raceway surface and rolling surface. Cycloidal shaped damage on the roller end. Scoring on rib surface contacting roller end.
Possible Cause
- Excessive load, excessive preload
- Poor lubrication
- Particles are caught in the surface
- Inclination of inner and outer rings
- Shaft bending
- Poor precision of the shaft and housing
Countermeasure
- Check the size of the load
- Adjust the preload
- Improve the lubricant and the lubrication method
- Check the precision of the shaft and housing

Part: Inner ring of a spherical roller bearing
Symptom: Scoring on large rib face of inner ring
Cause: Roller slipping due to sudden acceleration and deceleration

Part: Convex rollers
Symptom: Scoring on roller end face
Cause: Roller slipping due to sudden acceleration and deceleration

Part: Cage of a deep groove ball bearing
Symptom: Scoring on the pressed-steel cage pockets
Cause: Entry of debris

Part: Convex rollers of Photo 3.5
Symptom: Scoring on the roller end face
Cause: Debris, which is caught in surface, and excessive axial loading
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Scoring
Damage Condition
Scoring is surface damage due to accumulated small seizures caused by sliding under improper lubrication or under severe operating conditions. Linear damage appears circumferentially on the raceway surface and rolling surface. Cycloidal shaped damage on the roller end. Scoring on rib surface contacting roller end.
Possible Cause
- Excessive load, excessive preload
- Poor lubrication
- Particles are caught in the surface
- Inclination of inner and outer rings
- Shaft bending
- Poor precision of the shaft and housing
Countermeasure
- Check the size of the load
- Adjust the preload
- Improve the lubricant and the lubrication method
- Check the precision of the shaft and housing

Part: Outer ring
Symptom: Smearing occurs circumferentially on raceway surface
Cause: Roller slipping due to excessive grease filling

Part: Convex rollers
Symptom: Smearing occurs at the center of the rolling surface
Cause: Poor lubrication
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Cracks
Damage Condition
Cracks in the raceway ring and rolling elements. Continued use under this condition leads to larger cracks or fractures.
Possible Cause
- Excessive interference
- Excessive load, shock load
- Progression of flaking
- Heat generation and fretting caused by contact between mounting parts and raceway ring
- Heat generation due to creep
- Poor taper angle of tapered shaft
- Poor cylindricality of shaft
- Interference with bearing chamfer due to a large shaft corner radius
Countermeasure
- Correct the interference
- Check the load conditions
- Improve the mounting method
- Use an appropriate shaft shape

Part: Outer ring of a double-row cylindrical roller bearing
Symptom: Thermal cracks occur on the outer ring side face
Cause: Abnormal heat generation due to contact sliding
between mating part and face of outer ring

Part: Roller of a tapered roller thrust bearing
Symptom: Thermal cracks occur at large end face of roller
Cause: Heat generation due to sliding with the inner ring rib
under poor lubrication
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Pitting
Damage Condition
The pitted surface has a dull luster which appears on the rolling element surface or raceway surface.
Possible Cause
- Debris becomes caught in the lubricant
- Exposure to moisture in the atmosphere
- Poor lubrication
Countermeasure
- Improve the sealing mechanism
- Filter the lubrication oil thoroughly
- Use a proper lubricant

› Improve the sealing mechanism
› Filter the lubrication oil thoroughly
› Use a proper lubricant

Part: Ball
Symptom: Pitting occurs on the rolling element surface
Bearing Damage and Countermeasures: Wear
Damage Condition
Possible Cause
- Entry of debris
- Progression from rust and electrical corrosion
- Poor lubrication
- Sliding due to irregular motion of rolling elements
Countermeasure
- Improve the sealing mechanism
- Clean the housing
- Filter the lubrication oil thoroughly
- Check the lubricant and lubrication method
- Prevent misalignment

Part: Outer ring of a spherical roller bearing
Symptom: Wear having a wavy or concave-and-convex texture on loaded
side of raceway surface
Cause: Entry of debris under repeated vibration while stationary

Part: Tapered rollers of Photo 10.3
Symptom: Stepped wear on the roller head and face
Cause: Fretting progression due to excessive load while stationary
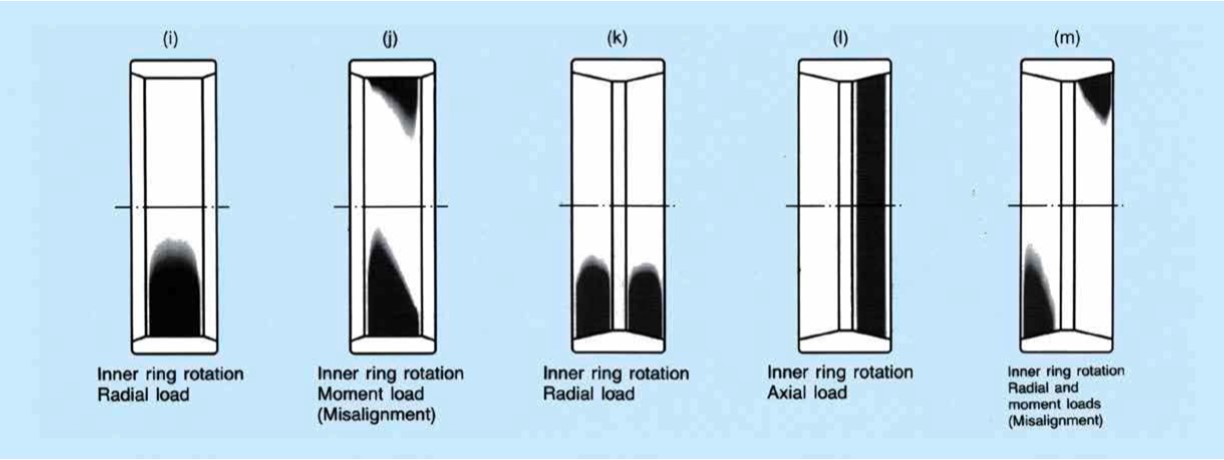
Typical running traces of deep groove ball bearings
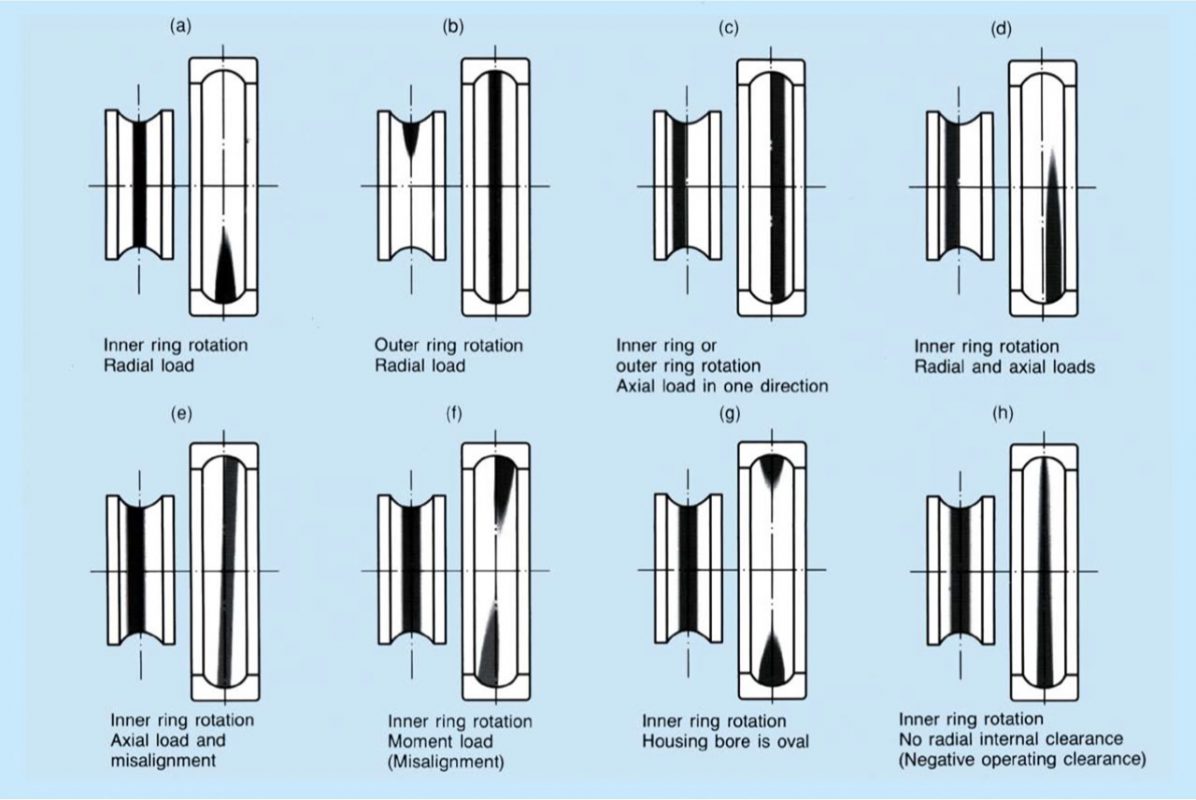
Typical running traces on roller bearings